With every passing year, there are more and more mobile phone users worldwide. By 2021, there will be 3.8 billion smartphone users, up from 2.5 billion in 2016. That represents incredible growth; and an incredible opportunity for cybercriminals.
About half of the world’s population uses smartphones. Those small devices hold an astonishing amount of sensitive personal data – emails, contact lists, health apps, online payments, social media, and passwords galore. The more daily activities people do on their phones, the more vulnerable those devices become in the war against cyber terrorism. And make no mistake, it’s a huge war.

In 2019, malware attacks on mobile phones increased by 50%, largely driven by the rise of personal banking apps. Social media apps have long been causing privacy concerns. TikTok, for example, has recently raised security concerns regarding privacy issues to the point that the U.S. Army has banned soldiers from using it.
With mobile phones increasingly becoming targets for hackers who want to steal personal data and defraud people, it is essential to secure your smartphone.
READ: Biometric Identification: The Good and The Bad
Smartphones Need Smart Security
Smartphones are fertile ground for hackers because there are so many ways to access them. The explosion of the use of apps led people to download all sorts of free apps and programs that do not have the best security protocols in place. People often leave apps running in the background on their phones without even realizing it, creating an opportunity for hackers to get in the back door. The use of mobile email also creates a huge opening for hackers to access smartphone data with spam and phishing attacks.
According to Kaspersky, a mobile antivirus company, there are seven types of dangers lurking for those who don’t properly secure their mobile phones. Some of these – such as unsecured WiFi – threaten regular desktop devices; however, others are exclusive to mobile phones.
For example, when installing an app, it requests permission to access your data and carry out certain actions on the phone. When a user grants an app all of these permissions, this can lead to “data leakage.” Data leakage is when an app unnecessarily exposes its users’ data because security protocols are insufficient.
To prevent data leakage, mobile phone users should always grant the minimum permissions needed to run an app properly. For instance, if you don’t need to create videos with an app, don’t allow it to access your camera and video library.
Tips for Securing Your Mobile Phone
Cybercriminals resort to complex measures to hack your mobile phone, but keeping your phone secure doesn’t have to be as complicated, thanks to advanced cybersecurity tools and a good dose of common sense. There are plenty of free antivirus apps available for mobile phones, with options to upgrade to more advanced versions.

Here are several basic tips for securing your mobile phone:
Make sure to use passwords
Locking your phone with a password is the frontline of defense for mobile phone security. Today, there are also biometric password options, such as fingerprint, iris (eye), or facial recognition. In addition to protecting the phone itself, any app or account you use on your phone should have separate and high-quality passwords.
Use double authentication when you can. This security method requires you to enter a password, and the app then sends you a new passcode via SMS or email that you must enter to gain access. Double authentication creates an extra barrier to entry, making it much harder for hackers to break through.
FIDO Alliance is leading the charge for mobile phone security and essentially replaces password-only across websites and apps for a more seamless and secure experience.
Remember to change passwords now and again to stay ahead of would-be hackers.
Install antivirus software
Antivirus software is a must for every connected device, including your smartphone. There are many different security apps for mobile devices; it’s just a matter of choosing the right one and downloading it to your phone.
The antivirus software runs periodic scans, but it is also important to run comprehensive scans now and then to ensure thorough protection. New viruses and threats pop up all the time, so be sure to update your antivirus software with the latest versions.
Do not use unprotected WiFi networks
This is a standard practice to secure any computer or mobile device. Beware of open or public WiFi services that could threaten your smartphone. Use your data plan for mobile access instead of connecting your phone to a less-than-secure network.
If you must use a free or public WiFi network, check that it is a secured network before connecting. You may want to install a VPN service on your phone to stay completely hidden and protected when using a public network.
Do not use suspicious-looking apps or websites
With nearly 9 million apps in the world, and with many being free, the temptation to install all kinds of apps is high. However, apps are one of the doors that hackers use to access your smartphone, so be cautious of what apps you download, what permissions you give those apps, and how you use them.
Like you would be careful not to visit a suspicious website, or click on unfamiliar links, the same goes for mobile apps. Make sure to use apps and visit mobile sites that are reputable and safe. Only download apps from proper app stores, like Google Play and the Apple App Store, and stay mindful of the information you share on apps and mobile sites. Most importantly, never provide personal or sensitive data to apps or emails that you can’t be sure are authentic.

Beyond the Phone
Any connected device is vulnerable to hacking. Many of your devices connect to the internet, making up the Internet of Things (IoT), and makes it easier for cybercriminals to access other devices connected to the same internet network. The IoT is the next frontier in cyber hacking. According to Symantec, IoT devices experience an average of over 5000 hacks every month.
To keep your information private, you want to create a secure moat around all your devices, including tablets, wearable tech, smart home hubs, etc. Don’t forget to make sure every household member’s devices are secured, including kids’ smartphones.
It is crucial to remember that common sense plays a huge role in keeping your device safe when it comes to smartphone security. Only connect with people and sites that you know, beware of small changes, like phishing scams that use fake logins to hijack access to your account, and don’t leave your phone unattended, even in situations that may seem trustworthy.
The image below is a perfect example of a phishing scam where hackers use well-known entities to trick targets into exposing their information. How many suspicious elements can you spot?
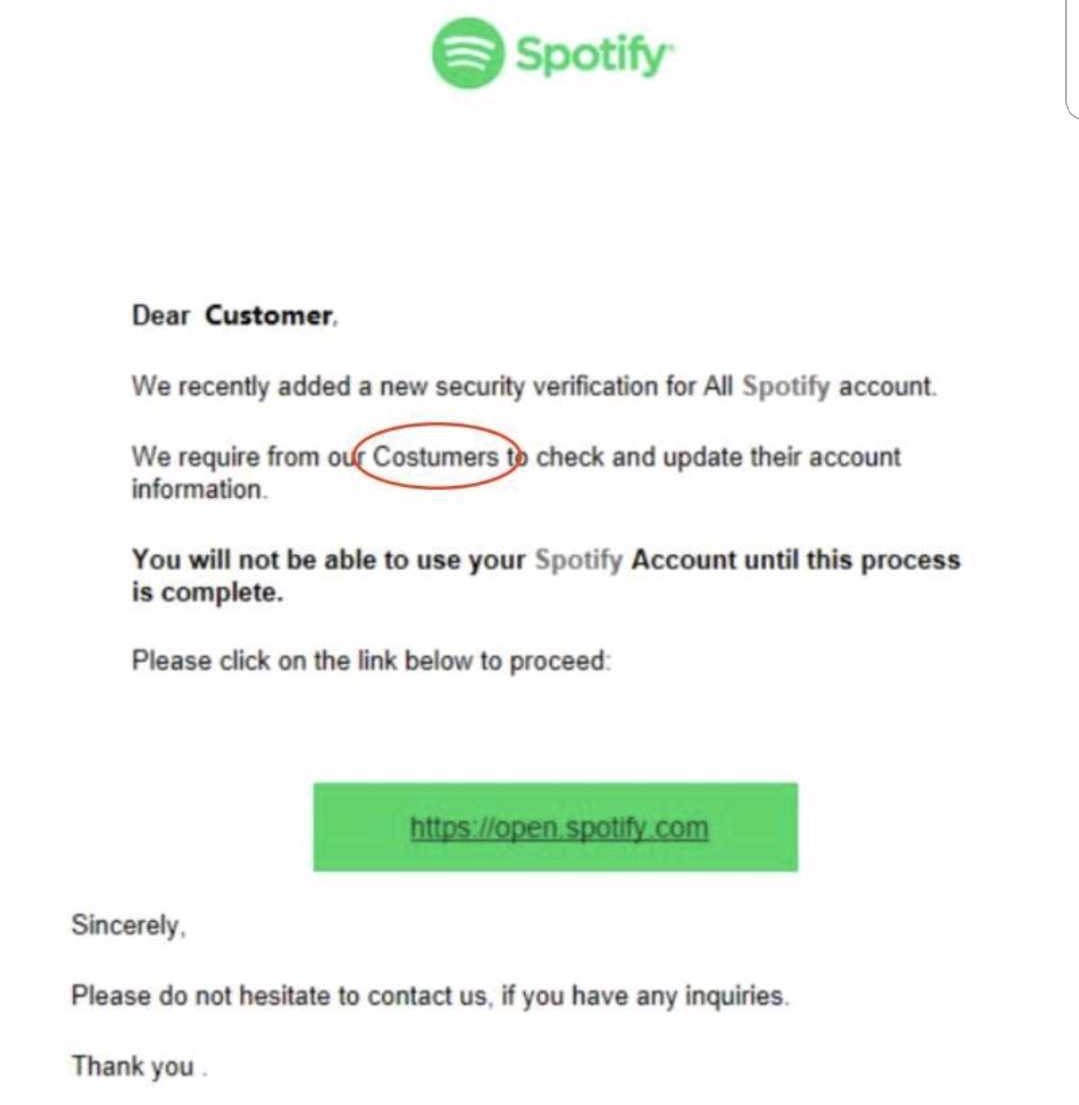
Think of your smartphone like your wallet—it contains vital, personal information, like credit cards, and cash—and you would never leave your wallet lying around. All these things can be accessed via your mobile phone by a sophisticated hacker, too! So be sure to act accordingly.
There’s something else that can help boost your security habits, and that’s education. Staying informed and up to date about your data security is key to keeping safe. But it can be much more than that, too.
Make Protection Your Career
As the world becomes ever more connected, via 5G smartphones and the Internet of Things, the knowledge and skills needed to combat cyberattacks also increase.
This leads to a quickly growing demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals who will continue the battle against cybercriminals in the years ahead. Learning everything there is to know about cybersecurity will protect you and your family’s smartphones—it can also become an exciting, challenging, and well-paying career.
Get started with our Cybersecurity Professional Bootcamp and get a job on the front line of the tech war raging on our smartphones and beyond.



